This is post 2 of 2 on diabetes. If you have NOT read the first post, please do it now!
Treatments and drugs
Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral medications may play a role in your treatment. A pancreas transplant may be an option for select people.
But no matter what type of diabetes you have, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising and keeping a healthy weight are all keys to managing your diabetes.
Treatments for all types of diabetes
An important part of managing all types of diabetes includes maintaining a healthy weight through a healthy diet and exercise plan:
Healthy eating. Contrary to popular perception, there’s no diabetes diet. You won’t be restricted to boring, bland foods. Instead, you’ll need plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grains — foods that are high in nutrition and low in fat and calories — and fewer animal products and sweets. In fact, it’s the best eating plan for the entire family. Even sugary foods are OK once in a while, as long as they’re included in your meal plan.
Yet understanding what and how much to eat can be a challenge. A registered dietitian can help you create a meal plan that fits your health goals, food preferences and lifestyle. Once you’ve covered the basics, remember the importance of consistency. To keep your blood sugar on an even keel, try to eat the same amount of food with the same proportion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats at the same time every day.
Physical activity. Everyone needs regular aerobic exercise, and people who have diabetes are no exception. Exercise lowers your blood sugar level by transporting sugar to your cells, where it’s used for energy. Exercise also increases your sensitivity to insulin, which means your body needs less insulin to transport sugar to your cells. Get your doctor’s OK to exercise. Then choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming or biking. What’s most important is making physical activity part of your daily routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes or more of aerobic exercise most days of the week. If you haven’t been active for a while, start slowly and build up gradually.
Treatments for type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes primarily involves monitoring of your blood sugar along with insulin, other diabetes medications or both.
Monitoring your blood sugar. Depending on your treatment plan, you may check and record your blood sugar level several times a week to several times a day. Careful monitoring is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level remains within your target range.
Even if you eat on a rigid schedule, the amount of sugar in your blood can change unpredictably. With help from your diabetes treatment team, you’ll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to things like food, physical activity, medications, illness, alcohol, stress and — for women — fluctuations in hormone levels.
In addition to daily blood sugar monitoring, your doctor may recommend regular A1C testing to measure your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. Compared with repeated daily blood sugar tests, A1C testing better indicates how well your diabetes treatment plan is working overall. An elevated A1C level may signal the need for a change in your insulin regimen or meal plan. Your target A1C goal may vary depending on your age and various other factors. However, for most people, the American Diabetes Association recommends an A1C of below 7 percent. Ask your doctor what your A1C target is.
Insulin. Anyone who has type 1 diabetes needs insulin therapy to survive. Some people with type 2 diabetes need insulin, as well. Because stomach enzymes interfere with insulin taken by mouth, oral insulin isn’t an option for lowering blood sugar. Often, insulin is injected using a fine needle and syringe or an insulin pen — a device that looks like an ink pen, except the cartridge is filled with insulin.
An insulin pump also may be an option. The pump is a device about the size of a cell phone worn on the outside of your body. A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter that’s inserted under the skin of your abdomen. The pump is programmed to dispense specific amounts of insulin automatically. It can be adjusted to deliver more or less insulin depending on meals, activity level and blood sugar level.
Many types of insulin are available, including rapid-acting insulin, long-acting insulin and intermediate options. Depending on your needs, your doctor may prescribe a mixture of insulin types to use throughout the day and night.
Oral or other medications. Sometimes other oral or injected medications are prescribed as well. Some diabetes medications stimulate your pancreas to produce and release more insulin. Others inhibit the production and release of glucose from your liver, which means you need less insulin to transport sugar into your cells. Still others block the action of stomach enzymes that break down carbohydrates or make your tissues more sensitive to insulin. Your doctor might prescribe low-dose aspirin therapy to help prevent cardiovascular disease.
Transplantation. In some people who have type 1 diabetes, a pancreas transplant may be an option. Other types of transplants are being studied as well. With a successful pancreas transplant, you would no longer need insulin therapy. But pancreas transplants aren’t always successful — and the procedure poses serious risks. You’d need a lifetime of potent immune-suppressing drugs to prevent organ rejection. These drugs can have serious side effects, including a high risk of infection, organ injury and cancer. Because the side effects can be more dangerous than the diabetes, pancreas transplants are usually reserved for people whose diabetes can’t be controlled or those who have serious complications.
Treatment for gestational diabetes
Controlling your blood sugar level is essential to keeping your baby healthy and avoiding complications during delivery. In addition to maintaining a healthy diet and exercising, your treatment plan may include monitoring your blood sugar and, in some cases, using insulin.
Your health care provider will also monitor your blood sugar level during labor. If your blood sugar rises, your baby may release high levels of insulin — which can lead to low blood sugar right after birth.
Treatment for pre-diabetes
If you have pre-diabetes, healthy lifestyle choices can help you bring your blood sugar level back to normal or at least keep it from rising toward the levels seen in type 2 diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight through exercise and healthy eating can help.
Sometimes medications — such as the oral diabetes drugs metformin (Glucophage) and acarbose (Precose) — also are an option if you’re at high risk of diabetes. This includes if your prediabetes is worsening or you have cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease or polycystic ovary syndrome.
In other cases, medications to control cholesterol — statins, in particular — and high blood pressure medications are needed. Your doctor might prescribe low-dose aspirin therapy to help prevent cardiovascular disease. Healthy lifestyle choices remain key, however.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Diabetes is a serious disease. Following your diabetes treatment plan takes round-the-clock commitment. But your efforts are worthwhile. Careful management of diabetes can reduce your risk of serious — even life-threatening — complications.
Lifestyle for all diabetes
No matter what type of diabetes you have:
* Make a commitment to managing your diabetes. Learn all you can about diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. Establish a relationship with a diabetes educator, and ask your diabetes treatment team for help when you need it.
* Take care of your teeth. Diabetes may leave you prone to gum infections. Brush and floss your teeth at least twice a day. And if you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, schedule dental exams at least twice a year. Consult your dentist right away if your gums bleed or look red or swollen.
Lifestyle for type 1 and type 2 diabetes
In addition, if you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes:
* Identify yourself. Wear a tag or bracelet that says you have diabetes. Keep a glucagon kit nearby in case of a low blood sugar emergency — and make sure your friends and loved ones know how to use it.
* Schedule a yearly physical and regular eye exams. Your regular diabetes checkups aren’t meant to replace yearly physicals or routine eye exams. During the physical, your doctor will look for any diabetes-related complications, as well as screen for other medical problems. Your eye care specialist will check for signs of retinal damage, cataracts and glaucoma.
* Keep your immunizations up-to-date. High blood sugar can weaken your immune system. Get a flu shot every year, and get a tetanus booster shot every 10 years. Your doctor may recommend the pneumonia vaccine or other immunizations as well.
* Pay attention to your feet. Wash your feet daily in lukewarm water. Dry them gently, especially between the toes. Moisturize with lotion, but not between the toes. Check your feet every day for blisters, cuts, sores, redness or swelling. Consult your doctor if you have a sore or other foot problem that doesn’t start to heal within a few days.
* Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol under control. Eating healthy foods and exercising regularly can go a long way toward controlling high blood pressure and cholesterol. Medication may be needed, too.
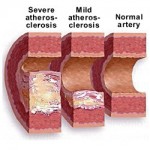
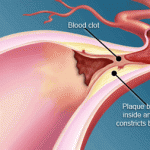
* If you smoke or use other types of tobacco, ask your doctor to help you quit. Smoking increases your risk of various diabetes complications, including heart attack, stroke, nerve damage and kidney disease. In fact, smokers who have diabetes are three times more likely to die of cardiovascular disease than are nonsmokers who have diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association. Talk to your doctor about ways to stop smoking or to stop using other types of tobacco.
* If you drink alcohol, do so responsibly. Alcohol can cause either high or low blood sugar, depending on how much you drink and if you eat at the same time. If you choose to drink, do so only in moderation and always with a meal. Remember to include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily calorie count.
* Take stress seriously. If you’re stressed, it’s easy to abandon your usual diabetes management routine. The hormones your body may produce in response to prolonged stress may prevent insulin from working properly, which only makes matters worse. To take control, set limits. Prioritize your tasks. Learn relaxation techniques. Get plenty of sleep. There is a great ebook you need to read on stress that will make a huge difference if you follow it. It is called the “The Little Book of Stress” and you can find it at http://www.stress-help.info
Above all, stay positive. The good habits you adopt today can help you enjoy an active, healthy life with diabetes.
Essential Nutrients and Herbs to Take:
| Acetyl L Carnitine
500 mg twice daily, on an empty stomach. Take with water. Do not take with milk. Take with B Complex and vitamin C (see below), for better absorption. Mobilizes fat. |
|
 |
L-Glutamine 500 mg 100 Caps
500 mg twice daily, on an empty stomach. Reduces the cravings for sugars |
 |
Taurine 500 mg 100 Caps
500 mg twice daily, on an empty stomach. Aids in the release of insulin. |
 |
Activated Quercetin
100 mg 3 times per day. Helps protect the membranes of the lenses of the eye from accumulations of polyols as a result of high glucose levels. |
 |
Biotin 5 mg 100 Caps
50 mg daily Improves the metabolism of glucose. |
 |
ANTI-OXIDANT, NATURAL (60 Tablets) with CO-ENZYME Q10
As directed Improves circulation and stabilizes blood sugar. |
 |
Alternative Health & Herbs Remedies Huckleberry, 1-Ounce Bottle (Pack of 2)
Huckleberry helps to promote insulin production. Take as directed. |
 |
Alternative Health & Herbs Remedies Cedar Berry 2 Ounces (Pack of 2)
Excellent nourishment for the pancreas. Take as directed. |
 |
Vitamin B Complex – B vitamins help to maintain the health for the nerves, skin, eyes, hair, liver. B-complex vitamins are coenzymes involved in energy production and may be useful in alleviating depression or anxiety.
Take 50 mg 3 times a day with meals. |
 |
Brewer’s Yeast – Improves insulin’s efficiency, which lowers blood sugar levels. This includes a combination of vitamins and minerals that work synergistically to regulate blood sugar levels and correct deficiencies. If you have diabetes, consult with your physician before taking any supplements containing chromium.
Take as directed on label. Start with 1 tsp daily and work up to 2 tbsp daily over a 2 -week period. |
Please check with your doctor before taking any supplements, and also read the warning labels on each product, especially if you are pregnant or breast-feeding. Also read the labels carefully when giving your child any natural supplement, to ensure that it is safe to give a child.
Prevention
Type 1 diabetes can’t be prevented. However, the same healthy lifestyle choices that help treat prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes can help prevent them.
* Eat healthy foods. Choose foods low in fat and calories. Focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Strive for variety to prevent boredom.
* Get more physical activity. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate physical activity a day. Take a brisk daily walk. Ride your bike. Swim laps. If you can’t fit in a long workout, break it up into smaller sessions spread throughout the day.
* Lose excess pounds. If you’re overweight, losing even 5 percent of your body weight — for example, 10 pounds (4.5 kilograms) if you weigh 200 pounds (90.7 kilograms) — can reduce the risk of diabetes. To keep your weight in a healthy range, focus on permanent changes to your eating and exercise habits. Motivate yourself by remembering the benefits of losing weight, such as a healthier heart, more energy and improved self-esteem.
Is Diabetes Reversal Possible?
Reversal of diabetes is possible! But let me be more specific so I can be completely accurate. When I talk about “Diabetes Reversal” I’m talking about trying to put the diabetes into REMISSION, meaning that the blood sugar levels are normal without diabetes medication. In other words, the disease is undetectable. I also refer to only Type 2 diabetes, about 80% to 90% of all diabetes is type 2 diabetes, and is associate with being overweight or obese. I am NOT referring to type 1 diabetes.
Here is what you have to do to have a chance of recersing diabetes:
Stop smoking!
You should immediately start to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Water acts a flusher of the body and begins to make it run more effectively. Healthier cells are also a byproduct of always staying hydrated. Men should drink at least 12 cups a day and women should drink at least 9 cups.
You should also look at your diet differently. Eat a high complex-carbohydrate, low fat, high fiber diet including plenty of raw fruits and vegetables as well as fresh vegetable juices. The British Broadcasting Company (BBC) ran the story on Aug. 5 2008 and translated it as: “Broccoli may undo diabetes damage.” This very interesting study looked at the phytochemical (plant compound) called sulforaphane. It seems to help produce enzymes in the body that protect blood vessels by reducing tissue damaging substances triggered by high blood sugar. Sulforaphane also seems to activate genes that regulate protective antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes. A diet consisting of the above foods reduces reduces the need for insulin and also lowers the levels of fats in the blood. Fiber helps to reduce blood sugar surges. For snacks, eat oat or rice bran crackers with nut butter or cheese. In addition, eat raw fruits and vegetables.
You should be trying to eat plenty of protein. Protein is necessary for cell membrane repair which can be responsible for the cells beginning to accept insulin again. Eating a diet that is high in protein is great for your body but even better for your diabetes. Best sources are grains, legumes, fish and low fat dairy products. Avoid saturated fats and simple sugars, except when necessary to balance an insulin reaction.
Exercising is extremely important because exercise helps create healthier cells that are not diabetic prone. Did you know that your body makes almost 100,000 new cells in a matter of seconds? The goal of your new lifestyle would be to create healthier cells! Eat more carbohydrates or reduce your insulin dosage before exercising. Exercise reduces an insulin like effect in the body. Talk to your doctor for details.
Take all of the above supplements, after talking to your doctor. They are an imperative part of combating diabetes.